

Pregnancies
Dear patients and parents to be,
We are pleased to offer midwife and medical care tailored to your specific needs during this special time in your life.
The practice has a particular focus on prenatal ultrasonic diagnosis. Through the full utilisation of the medical options and my extensive experience in the field of maternal medicine, you are assured a particularly secure provision of care during your pregnancy.
Prenatal diagnosis
Why prenatal diagnosis? All expectant parents ask themselves the question whether everything will "be fine" with their child. Will the child be healthy? Is the pregnancy developing normally? By modern Ultrasound Diagnostics, it is possible to answer these questions at an early stage to eliminate unnecessary fears. 2-4 % of all children are born with a malformation. The spectrum ranges from small abnormalities without significance to more severe malformations e.g. congenital heart failures. In the context of your child, it is beneficial if such findings are detected as early as possible, since the birth should be planed in specialised perinatal centres. In some cases, it is even possible to perform prenatal therapy as well as fetal surgery.
The regular ultrasound check-up in 10-12 weeks gestation (paid for by your health insurance) is only a rough orientation of the anatomy of the fetus. To achieve a high detection rate of abnormalities it requires a specific qualification of the medical examiner, a high-resolution ultrasound device and a special software from the Fetal Medicine Foundation, London. This service is offered by the Practice.
Today’s ultrasound technology makes it possible to have an assessment of individual structures already from 11 + 0 to 13 + 6 weeks of pregnancy. 65% of malformations can be found in the completed 12th or 13th week of pregnancy. An integrative part of the scan is the nuchal translucency. Nuchal translucency is the sonographic appearance of a collection of fluid under the skin behind the fetal neck. In fetuses with chromosomal abnormalities, cardiac defects and many genetic syndromes the nuchal translucency thickness is increased.
On the basis of this measurement and taking the maternal age and the time of pregnancy into account an individual statistical risk for Down Syndrome, Trisomy 13 and 18 can be calculated.
The detection rate of this investigation for Trisomy 21 is about 80% and can be increased by combining it with a Serum screening to approx. 85-90%. After the scan, the estimated risk factor for Down Syndrome will be discussed with you.
Only you can decide if you wish to have an invasive diagnostic test (chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis).
Irrespective of whether or not you decide to have an invasive test, it is recommended that you have a scan at 20 weeks to check for physical abnormalities.

Down Syndrome is named down after the Englishman Langdon, who described the image of a trisomy 21, for the first time in 1866. Down Syndrome is a genetical disorder which effects the mental and physical development of the child. The chromosome 21 is tripled, instead of the normal double set of chromosomes. People with Down Syndrome have 47 instead 46 chromosomes in every cell of their body. This occurs purely by chance and occurs about once in 600 births.
The older a woman gets the higher is her risk of having a child with Down Syndrome.
Children with Down Syndrome need our special attention during pregnancy and the family will need support after birth.
Once the child grows there will be a noticeable difference with the mental and physical development of the child. This does not however mean that the child will be dependant on state care. There are many examples of Down Syndrome adults leading an integral role in society.
For more information: www.down-kind.de
This is a detailed scan at 20-24 weeks of pregnancy.
During the scan we examine each part of the fetal body, determine the position of the placenta, assess the amount of amniotic fluid and measure the fetal growth. Special attention is paid to the brain, face, spine, heart, stomach, bowels, kidneys and limbs.
If any abnormalities are detected the significance of the findings will be discussed with other specialists in prenatal diagnosis and with paediatricians.
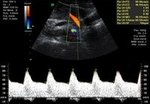
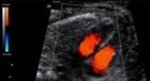
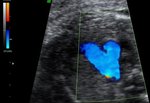
The Doppler measures the blood flow in the mothers uterine arteries and various vessels of the fetus. With this method, women with higher risk for placental insufficiency, fetal growth restriction or pre-eclampsia (pregnancy-related high blood pressure and urine protein excretion) can be detected already in early pregnancy. While women from the high risk group are often monitored, the number of inquiries in the group with low-risk decreases. The supply of the fetus with nutrients can be assessed by measuring the Doppler profile of the feto-maternal unit. Particularly for fetuses with growth restriction this method is essential for monitoring the child's development.
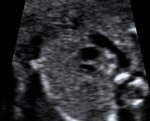
This is a detailed examination of the fetal heart and the connecting vessels. Congenital heart failure is found in 1% of newborns and therefore the most common congenital abnormality. An exact diagnosis in early pregnancy allows an early consultation with a children's cardiologists to guarantee optimal support of the child before and after birth. The delivery of children with congenital heart failure is planned in specialised centres. This scan is especially recommended for women with a family history of heart abnormalities, Diabetes or where increased nuchal translucency was found at the 12 week scan.
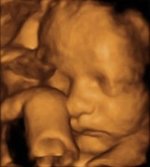
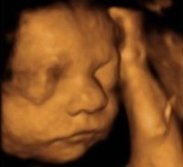
The plastic, three-dimensional representation of the fetal surface will give parents a fascinating image of their unborn child.
Since July 2013 it is possible to detect Trisomy 21,13 and 18 by a blood sample of the mother. The test is examining cell free DNA of the fetus that is circulating in the mothers blood.
Before this test can be performed you have to undergo First trimester screening and see a Consultant that is specialized in genetics.
The pubic health insurance decides on an individual basis as to weather or not they will pay for the test.
When is it sensible to carry out the PraenaTest®?
Carrying out the PrenaTest® is optional. Doing so makes sense if you belong to a risk group or if one of the mentioned trisomies is suspected in your unborn child based on ultrasound findings or previous blood tests. Please consult your physician about how high your personal risk is that your unborn child carries a trisomy 13, 18 or 21.
